Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Carbon and Its Compounds
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Carbon and Its Compounds
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:220
Question 1:
Name the element whose one of the allotropic forms is buckminsterfullerene.
Solution :
Carbon
Question 2:
What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the formation of a large number of carbon compounds ?
Solution :
Catenation(Self linking of carbon atoms to form long chains) and Tetravalency.
Question 3:
State whether the following statement is true or false :
Solution :
False
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:221
Question 4:
Name the scientist who disproved the ‘vital force theory’ for the formation of organic compounds.
Solution :
Friedrich Wohler.
Question 5:
Name the element whose allotropic form is graphite.
Solution :
Carbon.
Question 6:
In addition to some propane and ethane, LPG cylinders contain mainly two isomers of another alkane. Name the two isomers and write their condensed structural formulae.
Solution :
n-butane and iso-butane.
Question 7:
Buckminsterfullerene is a spherical molecule in which 60 carbon atoms are arranged in interlocking hexagonal and pentagonal rings of carbon atoms.
How many hexagons of carbon atoms are present in one molecule of buckminsterfullerene ?
How many pentagons of carbon atoms are present in one molecule of buckminsterfullerene ?
Solution :
(a) 20 hexagons
(b) 12 pentagons
Question 8:
Name the black substance of pencil. Will the current flow through the electrical circuit when we use the sharpened ends of the pencil to complete the circuit ?
Solution :
Graphite
Yes, current will flow through the circuit since graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
Question 9:
How does graphite act as a lubricant ?
Solution :
Graphite is used as a lubricant in the form of graphite powder or mixed with petroleum jelly or with any lubricant oil to form graphite grease.
Question 10:
Name the hardest natural substance known.
Solution :
Diamond
Question 11:
Which of the following molecule is called buckminsterfullerene ?
C90 C60 C70 C20
Solution :
C60 is called buckminsterfullerene
Question 12:
Give the name and structural formula of an alkyl group.
Solution :
Methyl
Question 13:
Write the electron-dot structures for : (i) ethane, (ii) ethene, and (iii) ethyne.
Solution :
Question 14:
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound :
C2H6
Solution :
Ethane.
Question 15:
Write the structural formula of propene.
Solution :
Question 16:
Write the structural formula of propyne.
Solution :
Question 17:
Write the structural formula of butane.
Solution :
Question 18:
What do you call the compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of atoms ?
Solution :
Isomers.
Question 19:
Write the names of any two isomers represented by the molecular formula C5H12.
Solution :
Isopentane and neopentane.
Question 20:
Write down (i) structural formula, and (ii) electron-dot formula, of any one isomer of hexane (C6H14), other than n-hexane.
Solution :
(i) Isomer of hexane: 2-methylpentane
Question 21:
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
(a) The form of carbon which is known as black lead is……………………..
(b) The form of carbon which is used as a lubricant at high temperature is……………………………
(c) Compounds of carbon with hydrogen alone are called…………………..
(d) CnH2n is the general formula of………………..
(e) Hydrocarbons having the general formula CnH2n-2 are called……………………..
(f) Ethene and ethyne are examples of…………….. hydrocarbons.
(g) Ethyne has…….. carbon-hydrogen single bonds.
(h) Carbon compounds have usually……………….. melting points and boiling points because they are……………… in nature.
(i) The property of carbon atoms to form long chains in compounds is called…………………………
(j) The general formula CnH2n for cycloalkanes is the same as that of……………………..
(k) The IUPAC name of ethylene is……………….
(l) The IUPAC name of acetylene is……………..
Solution :
(a) Graphite
(b) Graphite
(c) Hydrocarbons
(d) Alkene
(e) Alkynes
(f) Unsaturated
(g) Two
(h) Low; covalent
(i) Catenation
(j) Alkenes
(k) Ethene
(l) Ethyne
Question 22:
(a) What is the atomic number of carbon. Write its electronic configuration.
(b) What type of chemical bonds are formed by carbon ? Why ?
(c) Name the three allotropic forms of carbon.
Solution :
(a)The atomic number of carbon is 6. Its electronic configuration is 2,4.
(b)Carbon forms covalent bonds because it can achieve the inert gas electron arrangement only by sharing of electrons.
(c)Diamond, graphite and buckminsterfullerene.
Question 23:
(a) What is the general name of all the compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen ?
(b) Why does carbon form compounds mainly by covalent bonding ?
Solution :
(a) Hydrocarbons
(b) Carbon forms covalent bonds because it can achieve the inert gas electron
arrangement only by sharing of electrons.
Question 24:
(a) What is meant by catenation ? Name two elements which exhibit the property of catenation.
(b) Write the names and structural formulae of all the possible isomers of hexane.
Solution :
(a) The property of self combination of carbon atoms to form long chains is called catenation. Carbon and Silicon exhibit the property of catenation.
Question 25:
(a) What is buckminsterfullerene ? How is it related to diamond and graphite ?
(b) Why is diamond used for making cutting tools (like glass cutters) but graphite is not ?
(c) Why is graphite used for making dry cell electrodes but diamond is not ?
Solution :
(a) Buckminsterfullerene is an allotrope of carbon containing clusters of 60 carbon atoms joined together to form spherical molecules. It burns on heating to form carbon dioxide and nothing is left behind. This shows that it is made up of carbon only like diamond and graphite.
(b) Diamond used for making cutting tools but graphite is not because diamond is a very hard substance and graphite is a soft substance.
(c) Graphite is used for making dry cell electrodes but diamond is not b ecause graphite is a good conductor of electricity whereas diamond is a bad conductor of electricity.
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:222
Question 26:
(a) Give the general formula of an : (i) alkane (ii) alkene (in) alkyne.
(b) Classify the following compounds as alkanes, alkenes and alkynes :
C2H4, C3H4, C4H8, C5H12, C5H8, C3H8, C6H6
Solution :
(a) (i) CnH2n+2
(ii) CnH2n
(iii) CnH2n-2
Alkanes:
C5H12
C3H8
Alkenes:
C2H4
C4H8
Alkynes:
C3H4
C5H8
Question 27:
(a) Friedrich Wohler converted an inorganic compound into an organic compound in the laboratory.
(i) Give the name and formula of inorganic compound.
(ii) Write the name and formula of organic compound formed.
(b) Give the molecular formula of butane and mention the names of its two isomers. Name one fuel which contains both these isomers.
Solution :
(a) (i) Ammonium
cyanate, NH4CNO
(ii) Urea, CO(NH2)2
(b) The molecular
formula of butane is C4H10; Its isomers are n-butane
and 2-methylpropane; LPG.
Question 28:
(a) Give IUPAC names and formulae of an organic compound containing single bonds and the other
containing a triple bond.
(b) Which of the following is the molecular formula of benzene ?
C6H6, C6H10, C6H12, C6H14
(c) Which of the two has a branched chain : isobutane or normal butane ?
Solution :
(a) Methane (single bond):
CH4
Ethyne (triple bond): C2H2
(b) Benzene: C6H6
(c) Isobutene
Question 29:
Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon. Compare the ability of catenation of the two elements. Give reasons.
Solution :
Carbon forms strong bonds among themselves and with other elements and this makes the carbon compounds stable whereas silicon shows catenation property due to which it forms compounds with hydrogen having chains of up to 7 or 8 silicon atoms; but due to weak bonds, these compounds are unstable.
Question 30:
(a) How can diamonds be made artificially ? How do synthetic diamonds differ from natural ones ?
(b) Give any two differences between the properties of diamond and graphite. What causes these differences ?
Solution :
(a)Diamonds can be made artificially by subjecting pure carbon to very high
pressure and temperature. The synthetic diamonds are small whereas natural
diamonds are big.
(b)(i) Diamond is hard whereas graphite is soft.
(ii)Diamond is a non-conductor of electricity whereas graphite is a good conductor of electricity. The difference in the physical properties of diamond and graphite arises because
of the different arrangements of carbon atoms in them.
Question 31:
(a) Why does the element carbon from a large number of carbon compounds ?
(b) Write down the structures and names of two isomers of butane (C4H10)
Solution :
(a) Carbon forms a large number of carbon compounds because carbon atoms can link with one another by means of covalent bonds to form long chains of carbon atoms.
Question 32:
(a) Give the name and structural formula of one member each of the following :
(i) alkane (ii) alkene (iii) alkyne (iv) cycloalkane
(b) Give the common name of (i) ethyne, and (ii) ethene.
(c) Write the molecular formula and structure of benzene.
Solution :
(b) (i) Acetylene
(ii) Ethylene
(c) C6H6;
Question 33:
(a) What is the unique property of carbon atom ? How is this property helpful to us ?
(b) Explain why, diamond is hard while graphite is soft (though both are made of carbon atoms).
Solution :
(a) The most unique property of carbon atom is its ability to combine itself, atom to atom to form long chains. This property of self combination is useful to us because it gives rise to an extremely large number of carbon compounds (or organic compounds).
(b) A diamond crystal is a giant molecule of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom in the diamond crystal is linked to four other carbon atoms by strong covalent bonds. The four surrounding atoms are at the four vertices of a regular tetrahedron. This rigid structure of diamond makes it a very hard substance.
The structure of graphite is very different from that of diamond. A graphite crystal consists of layers of carbon atoms or sheets of carbon atoms and these layers are held together by weak Van der Waals forces. Due to this sheet like structure, graphite is a comparatively soft substance.
Question 34:
(a) Giving their structures, state the number of single bonds, double bonds and triple bonds (if any) in the following compounds :
(i) ethyne (ii) ethene (iii) benzene
(b) Write the molecular formula and structure of cyclohexane. How many covalent bonds are there in a molecule of cyclohexane ?
Solution :
(a) (i) Ethyne:- Single bonds: Two; Triple bond: One
(ii) Ethene:- Single bonds: Four; Double bond: One
(iii) Ethane:- Single bonds: Nine; Double bonds: Three
Question 35:
(a) Write two points of difference in the structures of diamond and graphite.
(b) Explain why, graphite can be used as a lubricant but diamond cannot.
(c) Explain why, diamond can be used in rock drilling equipment but graphite cannot.
(d) State one use of diamond which depends on its ‘extraordinary brilliance’ and one use of graphite which depends on its being ‘black and quite soft’.
Solution :
(a)
Diamond:
(i) Each carbon atom is linked to four other carbon atoms.
(ii) A diamond crystal has a tetrahedral arrangement of carbon atoms.
Graphite:
(i) Each carbon atom is joined to only three other carbon atoms.
(ii) A graphite crystal has flat hexagonal rings structure.
(b) Due to its softness, powdered graphite can be used a lubricant whereas diamond being extremely hard can not be used as lubricant.
(c) Due to its rigid structure, diamond is the hardest known substance to man. Hence, it is used in rock drilling equipments but graphite is soft and hence not used in rock drilling equipments.
(d) Diamonds are used for making jewellery.
Graphite is used for making pencil cores or ‘pencil leads’.
Question 36:
(a) What is diamond ? Of what substance is diamond made ?
(b) Describe the structure of diamond. Draw a simple diagram to show the arrangement of carbon atoms in diamond.
(c) Explain why, diamond has a high melting point.
(d) State any two uses of diamond.
Solution :
(a) Diamond is a colourless transparent substance having extraordinary brilliance. It is made up of carbon.
(b) A diamond crystal is a giant molecule of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom in the diamond crystal is linked to four other carbon atoms by strong covalent bonds. The four surrounding carbon atoms are at the four vertices of a regular tetrahedron. This rigid structure of diamond makes it a very hard substance.
(c) Diamond has a high melting point because a lot of heat energy is required to break the network of strong covalent bonds in the diamond crystal.
(d) (i) Used in rock drilling equipment (ii) Used in making jewellery.
Question 37:
(a) What is graphite ? Of what substance is graphite made ?
(b) Describe the structure of graphite with the help of a labelled diagram.
(c) Why is graphite a good conductor of electricity but diamond is a non-conductor of electricity ?
(d) State any two uses of graphite.
Solution :
(a) Graphite is a greyish-black opaque substance. It is made up of carbon.
(b) The structure of graphite is very different from that of diamond. A graphite crystal consists of layers of carbon atoms or sheets of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom in a graphite layer is joined to other three carbon atoms by strong covalent bonds to form flat hexagonal rings. The various layers of carbon atoms in graphite are held together by weak Van der Waals forces. Due to this sheet like structure, graphite is a comparatively soft substance.
(c) Due to the presence of free electrons in a graphite crystal, it conducts electricity however; a diamond crystal does not have free electrons so it does not conduct electricity.
(d) (i) Used as a lubricant (ii) Used for making pencil leads.
Question 38:
(a) Explain the term ‘isomers’. Give one example of isomers.
(b) Write (i) structural formula, and (ii) electron-dot structure, of any one isomer of n-heptane (C7H16)
(c) Write IUPAC name of the compound having the formula n-C4H10.
(d) Give the IUPAC names for the following :
Solution :
(a) The organic compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures are known as isomers for ex: n-butane and iso-butane are isomers.
(c) Butane
(d) (i) 2-methylpropane
(ii) 2-methylbutane
(iii) Propene
(iv) Propyne
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:223
Question 39:
(a) What are hydrocarbons ? Explain with examples.
(b) Explain the meaning of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples each.
(c) Give the names and structural formulae of one saturated cyclic hydrocarbon and one unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon.
(d) Give one example of a hydrocarbon, other than pentane, having more than three isomers.
(e) How many isomers of the following hydrocarbons are possible ?
(i) C3H8 (ii) C4H10 (iii) C5H12 (iv) C6H14
Solution :
(a) A compound made up of hydrogen and carbon only is called a hydrocarbon (Hydrogen + Carbon= Hydrocarbon). For exampe: methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), ethene (C2H4), and ethyne (C2H2), all are hydrocarbons as they are made up of only two elements: carbon and hydrogen.
(b) Saturated Hydrocarbons: These are the ones in which the carbon atoms are connected by only single bonds. They are also known as alkanes.
Example: Methane (CH4) and ethane (C2H6)
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: These are the ones in which two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond or a triple bond.
Example: Ethene (C2H4) and ethyne (C2H2)
(c) Saturated cyclic hydrocarbon: Cyclohexane, C6H12
Unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon: Benzene, C6H6
(d) Hexane, C6H14
(e) (i) None (ii) Two (iii) Three (iv) Five
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:224
Question 60:
A solid element X has four electrons in the outermost shell of its atom. An allotrope Y of this element is used as a dry lubricant in machinery and also in making pencil leads.
(a) What is element X ?
(b) Name the allotrope Y.
(c) State whether allotrope Y is a good conductor or non-conductor of electricity.
(d) Name one use of allotrope Y (other than lubrication and pencil leads)
(e) Name two other allotropes of element X.
Solution :
(a) Element X : Carbon
(b) Allotrope Y: Graphite
(c) Y is a good conductor of electricity.
(d) Y is used for making graphite electrodes or carbon electrodes in dry cells.
(e) Allotropes of X: Diamond and buckminsterfullerene
Question 61:
Two organic compounds A and B have the same molecular formula C6H12. Write the names and structural formulae :
(a) if A is a cyclic compound
(b) if B is an open chain compound
(c) Which compound contains single bonds as well as a double bond ?
(d) Which compound contains only single bonds ?
Solution :
Question 62:
The solid element A exhibits the property of catenation. It is also present in the form of a gas B in the air which is utilised by plants in photosynthesis. An allotrope C of this element is used in glass cutters.
(a) What is element A ?
(b) What is the gas B ?
(c) Name the allotrope C.
(d) State another use of allotrope C (other than in glass cutters).
(e) Name another allotrope of element A which exists as spherical molecules.
(f) Name a yet another allotrope of element A which conducts electricity.
Solution :
(a) Element A: Carbon
(b) Gas B: Carbon dioxide
(c) Allotrope C: Diamond
(d) Used for making jewellery
(e) Buckminsterfullerene
(f) Graphite
Question 63:
An element E exists in three allotropic forms A, B and C. In allotrope A, the atoms of element E are joined to form spherical molecules. In allotrope B, each atom of element E is surrounded by three other E atoms to form a sheet like structure. In allotrope C, each atom of element E is surrounded by four other E atoms to form a rigid structure.
(a) Name the element E.
(b) What is allotrope A ?
(c) What is allotrope B ?
(d) What is allotrope C ?
(e) Which allotrope is used in making jewellery ?
(f) Which allotrope is used in making anode of a dry cell ?
Solution :
(a) Element E: Carbon
(b) Allotrope A: Buckminsterfullerene
(c) Allotrope B: Graphite
(d) Allotrope C: Diamond
(e) C
(f) B
Question 64:
You are given the following molecular formulae of some hydrocarbons :
C5H8; C7H4; C6H6; C5H10; C7 H12; C6H12
(a) Which formula represents cyclohexane as well as hexene ?
(b) Which formula represents benzene ?
(c) Which three formulae represent open chain unsaturated hydrocarbons having double bonds ?
(e) Which two formulae represent unsaturated hydrocarbons having triple bonds ?
(f) Which three formulae can represent cyclic hydrocarbons ?
Solution :
(a) C6H12
(b) C6H6
(c) C7H14;
C5H10; C6H12
(d) C5H8;
C7H12
(e) C7H14;
C5H10; C6H12
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:225
Question 65:
Which of the following compounds can have a triple bond ?
C2H4, C3H4, C3H6
Solution :
C3H4
Question 66:
Write the molecular and structural formula of a cyclic hydrocarbon whose molecule contains 8 atoms of carbon.
Solution :
Molecular formula: C8H16
Question 67:
What is the molecular formula and structural formula of a cyclic hydrocarbon whose one molecule contains 8 hydrogen atoms ?
Solution :
Molecular formula: C4H8
Question 68:
Write the molecular formula of : (i) an alkane (ii) an alkene, and (iii) an alkyne, each having 20 carbon atoms.
Solution :
(i) C20H42
(ii) C20H40 (iii) C20H38
Question 69:
Which of the following compounds can have a double bond ?
C4H10; C5H8; C5H10
Solution :
C5H10
Question 70:
Which of the following hydrocarbons is unsaturated ?
C3H4; C2H6
Solution :
C3H4
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:239
Question 1:
Write the molecular formula of ethanol.
Solution :
C2H5OH
Question 2:
What is the next higher homologue of methanol (CH3OH) ?
Solution :
Ethanol (C2H5OH)
Question 3:
Identify the functional group present in the following compound and name it according to IUPAC system :
CH3OH
Solution :
Alcohol group;
Methanol
Question 4:
Give the common name and IUPAC name of the simplest aldehyde.
Solution :
Common name:
formaldehyde
IUPAC name: methanal
Question 5:
What is the common name of methanal ?
Solution :
Formaldehyde
Question 6:
Write the names of the following functional groups :
Solution :
(i) Alkyne
(ii) Alkene
Question 7:
Name the simplest ketone.
Solution :
Propanone
Question 8:
What is the common name of propanone ?
Solution :
Acetone
Question 9:
Write the IUPAC names of the following :
(i) CH3COCH3 (ii) CH3COCH2CH3
Solution :
(i) Propanone
(ii) Butanone
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:240
Question 10:
Write the name and chemical formula of the simplest organic acid.
Solution :
Formic acid; HCOOH
Question 11:
Write the IUPAC names, common names and formulae of the first two members of the homologous series of carboxylic acids.
Solution :
Question 12:
What is the common name of : (a) methanoic acid, and (b) ethanoic acid ?
Solution :
(a) Methanoicacid – Formic acid
(b) Ethanoic acid – Acetic acid
Question 13:
Draw the structures for the following compounds :
(a) Ethanoic acid (b) Propanoic acid
Solution :
Question 14:
Give the common names and IUPAC names of the following compounds :
(a) HCOOH (b) CH3COOH
Solution :
Question 15:
Give the name and structural formula of one homologue of HCOOH.
Solution :
Ethanoic acid; CH3COOH
Question 16:
Write the formulae of: (a) methanoic acid, and (b) ethanoic acid.
Solution :
(a) Methanoic acid: HCOOH
(b) Ethanoic acid: CH3COOH
Question 17:
Give the common name and IUPAC name of C2H5
Solution :
Common name: Ethyl alcohol
IUPAC name: Ethanol
Question 18:
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound :
C3H7OPI
Solution :
Propanol, C3H7OH
Question 19:
Give the name and structural formula of one member of the following :
Alcohols
Solution :
Ethanol; C2H5OH
Question 20:
Give IUPAC names of the following compounds :
(a) C4H9OH (b) C5HnOH
Solution :
(a) Butanol, C4H9OH
(b) Pentanol, C5H11OH
Question 21:
What is the common name of methanol ?
Solution :
Methyl alcohol
Question 22:
What is the difference between two consecutive homologues :
(i) in terms of molecular mass ?
(ii) in terms of number and kind of atoms per molecule ?
Solution :
(i) 14 u
(ii) Two consecutive homologues differ by 1 carbon atom and 2 hydrogen atoms in their molecular formulae.
Question 23:
What type of fuels :
(a) burn with a flame ?
(b) burn without a flame ?
Solution :
(a) Fuels which vaporise on heating, burn with a flame.
(b) Fuels which do not vaporise on heating, burn without a flame.
Question 24:
State whether the following statement is true or false :
The minimum number of carbon atoms in a ketone molecule is two.
Solution :
False
Question 25:
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
(a) The next higher homologue of ethanol is……….
(b) The next homologue of C2H5OH is……….
(c) The next higher homologue of ethane is………..
(d) The functional group present in ethanol is……….
Solution :
(a) Propanol
(b) C3H7OH
(c) Propane
(d) -OH (alcohol)
(e) Carboxylic acids
Question 26:
(a) Give the general name of the class of compounds having the general formula CnH2n-2.Write name of the first member of this homologous series.
(b) The general formula of a homologous series of carbon compounds is CnH2n. Write the molecular formulae of the second and fourth members of the series.
(c) Write the molecular formulae of the third and fifth members of homologous series of carbon compounds represented by the general formula CnH2n+2.
Solution :
(a) Alkynes, CnH2n-2
First member: Ethyne
(b) Second member: C3H6
Fourth member: C5H10
(c) Third member: C3H8
Fifth member: C5H12
Question 27:
(a) Give the names and structural formulae of the next two higher homologues of methane.
(b) The molecular formula of a hydrocarbon is C10H18. Name its homologous series.
(c) Select the hydrocarbons which are members of the same homologous series. Give the name of each series.
C5H10 ; C3H8; C6H10; C4H10; C7H12; C8H16
Solution :
(a)
Question 28:
(a) Give the molecular formula of one homologue of each of the following :
(i) C3H6 (ii) C2H6 (iii) C2H2
(b) What is the difference in the molecular mass of any two adjacent homologues ?
(c) By how many carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms do any two adjacent homologues differ ?
Solution :
(a) (i) C4H8 (ii) C3H8
(iii) C3H4
(b) 14 u
(c) 1 carbon atom and 2 hydrogen atoms i.e. a CH2 group.
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:241
Question 29:
(a) Write the formula of the functional group present in carboxylic acids.
(b) Name the functional group present in CH3—C ≡ CH.
(c) Name the functional groups present in the following compounds :
(i) CH3CHO (ii) CH3CH2COOH (iii) CH3COCH3 (iv) CH3CH2CH2OH
Solution :
Question 30:
(a) Write the IUPAC name and common name of CH3CI
(b) Draw the structure of chlorobutane.
(c) Draw the structure for bromopentane. Are structural isomers possible for bromopentane ?
Solution :
Question 31:
(a) Write the name and formula of an organic compound containing a ketone functional group.
(b) Write the names and formulae for the first three members of the homologous series of chloroalkanes.
(c) How would you name the following compound ?
CH3—CH2—Br
Solution :
(a) Acetone – CH3COCH3
(b) (i) Chloromethane – CH3Cl
(ii) Chloroethane – C2H5Cl
(iii) Chloropropane – C3H7Cl
(c) Ethylbromide
(a) Ketones
(b) CH3COOH
(c) Formaldehyde
Question 33:
(a) Define a homologous series. Give the name and structural formula of one homologue of the following :
CH3OH
(b) Write the molecular formula of the third member of the homologous series of carbon compounds with general formula CnH2n+1OH.
(c) Name any two fossil fuels.
Solution :
Question 34:
(a) Draw the structures for the following compounds :
(a) Propanone (b) Butanone
(b) Write the IUPAC names of the following :
(i) HCHO (ii) CH3CHO (Hi) CH3CH2CHO (iv) CH3CH2CH2CHO
(c) Which functional group is likely to be present in an organic compound having the molecular formula C4H10O ? Write the formula of the organic compound.
Solution :
Question 35:
(a) Match the formulae in group A with appropriate names from group B :
Group A : CH3COOH, CH3CHO, CH3OH
Group B : Ethanol, Methanol, Ethanal, Ethanoic acid
(b) Draw the structure of butanoic acid.
(c) What is the IUPAC name of acetic acid ?
Solution :
Question 36:
(a) Which functional group do you think can be present in an organic compound having the molecular formula C5H10O2 ? Write the formula of the organic compound.
(b) Give one example each of the compounds having the following functional groups :
(i) Aldehyde group (ii) Alcohol group (iii) Carboxylic acid group (iv) Halo group
(c) Give one example each of the compounds having the following functional groups :
(i) Alkene group (ii) Alkyne group
Solution :
Question 37:
(a) What is the molecular formula and structure of the alcohol which can be thought to be derived from pentane ?
(b) Write the names of the following functional groups :![]()
(c) What makes the candle flame yellow and luminous ?
Solution :
(a) C5H12O or C5H11OH
(b) (i) Aldehyde group
(ii) Alcohol group
(iii) Carboxylic acid group
(iv) Ketone group
(v) Halo group
(c) When a candle is lighted, the wax melts, rises up the wick and gets converted into vapours. In a candle, there is no provision for the proper mixing of oxygen (of air) for burning wax vapours. So, the wax vapours bum in an insufficient supply of oxygen (of air) which leads to incomplete combustion of wax. This incomplete combustion of wax produces small unburnt carbon particles. These solid carbon particles rise in the flame, get heated and glow to give out yellowish light. This makes the candle flame yellow and luminous.
Question 38:
(a) What is a homologous series ? Explain with an example.
(b) State two characteristics of a homologous series.
(c) The molecular formula of an organic compound is C18H36. Name its homologous series.
(d) Select the hydrocarbons which belong to the same homologous series. Give the name of each series.
CH4, C2H2, C2H4, C2H6, C4H10, C3H4, C3H6
(e) What is meant by ‘heteroatom’? Give examples. Write the names and formulae of two organic compounds containing different heteroatoms.
Solution :
(a) A homologous series is a group of organic compounds having similar structures and similar chemical properties in which the successive compounds differ by CH2 group.
Example of Homologous series: All the alkanes have similar structures with single covalent bonds and show similar chemical properties, so they can be grouped together in the form of a homologous series.
Homologous series of alkanes: Methane, CH4; Ethane, C2H6; Propane, C3H8; Butane, C4H10; Pentane, C5H12
(b) (i) All the members of the homologous series can be represented by the same general formula.
(ii) Any two adjacent homologues differ by 1 carbon atom and 2 hydrogen atoms in their molecular formulae.
(c) Alkene, CnH2n
(d) Alkanes: CH4, C2H6, C4H10?
Alkenes :C2H4, C3H6
Alkynes : C2H2, C3H4
(e) In an organic compound, any atom other than carbon and hydrogen is called a heteroatom.
Example: Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Oxygen (O)
Chloromethane – CH3Cl and methanol – CH3OH
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:242
Question 39:
(a) What is meant by a functional group ? Explain with an example.
(b) Write three common functional groups present in organic compounds. Give their symbols/formulae.
(c) Name the functional groups present in the following compounds :
(i) CH3COOH (ii) CH3CH2CHO (iii) C2H5OH (iv) CH3COCH2CH3
(d) Name the functional group which always occurs in the middle of a carbon chain.
(e) Draw the structures for the following compounds :
(i) Ethanal (ii) Propanal (iii) Butanal (iv) Pentanal
Solution :
(a) An ‘atom’ or ‘a group of atoms’ which makes a carbon compound (or organic compound) reactive and decides its properties (or functions) is called a functional group. The alcohol group, -OH, present in ethanol, C2H5OH, is an example of a functional group.
(b) (i) Halo group: -X
(ii) Alcohol group: -OH
(iii) Aldehyde group: -CHO
(c) (i) Carboxylic acid group
(ii) Aldehyde group
(iii) Alcohol group
(iv) Ketone group
(d) Ketone group, -CO-
Question 40:
(a) What happens when carbon burns in air ? Write the chemical equation of the reaction which takes place.
(b) Why are coal and petroleum called fossil fuels ?
(c) Explain how coal was formed in the earth.
(d) Describe how petroleum was formed in the earth.
(e) Name a fossil fuel other than coal and petroleum.
Solution :
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:243
Question 56:
An organic compound having the molecular formula C2H60 can exist in the form of two isomers A and B having different functional groups. The isomer A is a liquid which is used as a solvent for nail polish. The isomer B is also a liquid. An aqueous solution of one of the lower homologues of B is used for preserving biological specimens in the laboratory
(a) What is compound A ?
(b) Write the electron-dot structure of A.
(c) What is compound B ?
(d) Write the electron-dot structure of B.
(e) Name the lower homologue of compound B which is used in preserving biological specimens.
Solution :
Question 57:
A hard material X which is mined from the earth is used as a household fuel and also for the generation of electricity at Thermal Power Stations. A soft material Y is also used as a fuel in the form of candles. A gaseous material Z which occurs along with petroleum is increasingly being used as a fuel in running vehicles in its compressed form.
(a) What are materials, X, Y and Z ?
(b) When materials X, Y and Z are burned separately :
(i) Which material burns by producing a yellow, luminous flame ?
(ii) Which material ultimately burns without producing a flame ?
(iii) Which material can burn in a gas stove by producing a blue flame ?
Solution :
(a) X is coal; Y is wax; Z is natural gas
(b)(i) Y (wax)
(ii) X (coal)
(iii) Z (natural gas)
Question 58:
Three organic compounds A, B and C have the following molecular formulae :
A C4H8O2
B C4H10O
C C4H8O
(a) Which compound contains an alcohol group ? Write its name and structural formula.
(b) Which compound contains a carboxyl group ? Write its name and structural formula.
(c) Which molecular formula can represent an aldehyde as well as a ketone ? Write the names and structural formulae of the aldehyde and ketone represented by this molecular formula.
Solution :
Question 59:
A colourless organic liquid X of molecular formula C2H402 turns blue litmus to red. Another colourless organic liquid Y of molecular formula C2H60 has no action on any litmus but it is used as a nail polish remover. A yet another colourless organic liquid Z of molecular formula C2H6O has also no action on litmus but it is used in tincture of iodine.
(a) Name the liquid X. To which homologous series does it belong ? Give the name of another member of this homologous series.
(b) Name the liquid Y. To which homologous series does it belong ? Write the name of another member of this homologous series.
(c) Can you name an organic compound having the same molecular formula as liquid Y but which belongs to a different homologous series ? What is this homologous series ?
(d) Name the liquid Z. To which homologous series does it belong ? Write the name of another member of this homologous series.
Solution :
(a) Liquid X is ethanoic acid; it belongs to homologous series of carboxylic acids. Methanoic acid is another member of this homologous series.
(b) Liquid Y is Propanone; it belongs to homologous series of ketones. Butanone is another member of this homologous series.
(c) Propanal; it belongs to homologous series of aldehydes.
(d) Liquid Z is ethanol; it belongs to homologous series of alcohols. Methanol is another member of this homologous series.
Question 60:
You are given an organic compound having the molecular formula C2H8. Give the name and formula of the compound formed :
(a) when one H atom of C3H8 is replaced by a Cl atom.
(b) when one H atom of C3H8 is replaced by OH group.
(c) when one H atom of C3H8 is replaced by a CHO group.
(d) when one H atom of C3H8 is replaced by a COOH group.
(e) when two H atoms joined to the middle carbon atom of C3H8 are replaced by one O atom.
Solution :
(a) Chloropropane, CH3-CH2-CH2-Cl
(b) Propanol, CH3-CH2-CH2-OH
(c) Butanal, CH3-CH2-CH2-CHO
(d) Butanoic acid, CH3-CH2-CH2-COOH
(e) Propanone, CH3-CO-CH3
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:262
Question 1:
Name the gas evolved when ethanoic acid is added to sodium carbonate. How would you prove the presence of this gas ?
Solution :
Carbon dioxide (CO2) gas is evolved in the reaction. When passed through lime water, it turns lime water milky.
Question 2:
Which of the following will give brisk effervescence with sodium hydrogencarbonate and why ? CH3COOH, CH3CH2OH
Solution :
CH3COOH will give brick effervescence. Being acid, it reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate to produce carbon dioxide gas.
Question 3:
Name the functional group present in an organic compound which gives brisk effervescence with NaHC03.
Solution :
Carboxylic acid group, -COOH gives brisk effervescence with NaHCO3
Question 4:
Name the hydrocarbon formed when ethanol is heated with cone. H2S04 at 170°C ? What is this reaction known as ?
Solution :
Ethene is formed when ethanol is heated with conc. H2SO4 at 170oC. This reaction is called dehydration.
Question 5:
Why does ethyne (acetylene) burn with a sooty flame ?
Solution :
Ethyne (acetylene) burn with a sooty flame because ethyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon and the percentage of carbon in these hydrocarbons is comparatively higher which does not get oxidised completely in oxygen of air.
Question 6:
Name the product formed when hydrogen is added to ethene.
Solution :
Ethane is formed when hydrogen is added to ethene.
Question 7:
Explain why, ethene decolourises bromine water whereas ethane does not.
Solution :
Ethene decolourises bromine water because ethene is an alkene. And all alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated compounds which decolourise bromine water. On the other hand, ethane being an alkane is a saturated compound which does not decolourise bromine water.
Question 8:
Name two catalysts which can be used in the hydrogenation of unsaturated compounds.
Solution :
Nickel or palladium can be used as catalyst in the hydrogenation of unsaturated compounds.
Question 9:
State two disadvantages of incomplete combustion.
Solution :
Disadvantages of incomplete combustion:
(i) It leads to the formation of soot which is nothing but unburnt carbon which pollutes the atmosphere, blackens cooking utensils.
(ii) It leads to the formation of an extremely poisonous gas called carbon monoxide.
Question 10:
What happens when (give chemical equation) :
Sodium reacts with ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
Solution :
Question 11:
Describe one reaction of ethanol.
Solution :
Question 12:
Name one liquid carbon compound which is being used as an additive in petrol in some countries.
Solution :
Ethanol is used as an additive in petrol.
Question 13:
What are the raw materials required for making soap in a laboratory (or at home) ?
Solution :
(i) Vegetable oil (like castor oil, cottonseed oil or soyabean oil)
(ii) Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda)
(iii) Sodium chloride (common salt)
Question 14:
Would you be able to check whether water is hard by using a detergent ? Why ?
Solution :
No, we would not be able to check the hardness of water by using a detergent because a detergent forms lather easily even with hard water.
Question 15:
Describe a test for carboxylic acids.
Solution :
Litmus test: Some blue litmus solution is added to the organic compound (to be tested). If the blue litmus solution turns red, it shows that the organic compound is acidic in nature and hence it is a carboxylic acid.
Question 16:
Why is the conversion of ethanol into ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction ?
Solution :
Question 17:
Explain why, alkanes are excellent fuels.
Solution :
Alkanes burn in air to produce a lot of heat due to which they are known to be excellent fuels.
Question 18:
Name one chemical compound which can be used to distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid.
Solution :
Sodium hydrogencarbonate can be used to distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid.
Question 19:
Complete the following equations :
Solution :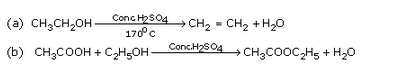
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:263
Question 20:
Complete and balance the following equations :
Solution :
Question 21:
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
(a) The process of burning of a hydrocarbon in the presence of air to give CO2, H2O, heat and light is known as………
(b) The sodium salt of a long chain fatty acid is called………………..
(c) is better than soap for washing clothes when the water is hard.
(d) The organic acid present in vinegar is………………..
Solution :
(a) Combustion
(b) Soap
(c) Detergent
(d) Ethanoic acid
Question 22:
Which of the following hydrocarbons will give substitution reactions and why ?
CH4, C3H6, C3H8, C4H6, C5H12, C5H10
Solution :
CH4, C3H8 and C5H12; all these are saturated hydrocarbons (Alkanes) and hence will give substitution reactions.
Solution 23
C2H4 and C3H4 will give addition reactions because these are unsaturated hydrocarbons (Alkene and Alkyne) and unsaturated hydrocarbons give addition reactions.
Question 24:
(a) Write the chemical equation of the reaction which takes place during the burning of ethanol in air.
(b) Why is ethanol used as a fuel ?
(c) State two uses of ethanol (other than as a fuel).
Solution :
(b) Since, ethanol burns with a clear flame giving a lot of heat, therefore, it is used as a fuel.
(c) Uses of ethanol:
(i) It is used in the manufacture of paints, varnishes, lacquers, medicines, perfumes, dyes, soaps and synthetic rubber.
(ii) It is used as a solvent. Many organic compounds which are insoluble in water are soluble in ethyl alcohol.
Question 25:
(a) What happens when propanoic acid is warmed with methanol in the presence of a few drops of
concentrated sulphuric acid ? Write equation of the reaction involved.
(b) What change will you observe if you test soap solution with a litmus paper (red and blue) ? Give reason for your observation.
(c) What is meant by denatured alcohol ? What is the need to denature alcohol ?
Solution :
(a) Propanoic acid will react with the alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid to form esters.![]()
(b) Red litmus paper turns blue in soap solution and no change occurs on blue litmus paper because soap is basic in nature.
(c) Denatured alcohol is ethyl alcohol which has been made unfit for drinking purposes by adding small amounts of poisonous substances like methanol, pyridine, copper sulphate etc. This is done to prevent the misuse of industrial alcohol for drinking purposes or black marketing (as it is supplied duty free for industrial purposes by the government).
Question 26:
(a) How would you test for an alcohol ?
(b) Give the harmful effects of drinking alcohol.
(c)Explain why, methanol is much more dangerous to drink than ethanol.
Solution :
(a) Sodium metal test: Add a small piece of sodium metal to the organic liquid (to be tested), taken in a dry test tube. If bubbles (or effervescence) of hydrogen gas are produced, it indicates that the given organic liquid is an alcohol.
(b) Harmful effects of drinking alcohol:
(i) Alcohol slows down the activity of the nervous system and brain due to which the judgement of a person is impaired and his reaction becomes slow.
(ii) Heavy drinking of alcohol on a particular occasion leads to staggered movement, slurred speech and vomiting.
(c) Unlike ethanol, drinking methanol, even in a small quantity can be fatal leading to permanent blindness and even death. Methanol damages the optic nerve causing permanent blindness in a person. This happens because methanol is oxidised to methanal in the liver of a person. This methanal reacts rapidly with the components of the cell causing coagulation of their protoplasm. Due to this, the cells stop functioning normally.
Question 27:
How would you convert:
(a) ethanol into ethene ?
(b) propanol into propanoic acid ?
Name the process in each case and write the equations of the reactions involved.
Solution :
Question 28:
Give reasons for the following observations :
(a) Air holes of a gas burner have to be adjusted when the vessels being heated get blackened by the flame.
(b) Use of synthetic detergents causes pollution of water.
Solution :
(a) Air holes of a gas burner have to be adjusted b ecause blackening of vessels show that the air holes of the gas stove are getting blocked and hence the fuel is not burning completely (due to insufficient supply of oxygen).
(b) Some of the detergents (synthetic) are not bio-degradable, that is they cannot be decomposed by micro organisms like bacteria and hence cause water pollution.
Question 29:
(a) What would be observed on adding a 5% alkaline potassium permanganate solution drop by drop to
some warm ethanol in a test-tube ? Write the name of the compound formed during the chemical reaction. Also write chemical equation of the reaction which takes place.
(b) How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid on the basis of a chemical property ?
Solution :
(a) On adding 5% alkaline potassium permanganate solution drop by drop to some warm ethanol, we would observe that the purple color of potassium permanganate starts disappearing; the product formed by this process; ethanoic acid can turn blue litmus red.![]()
(b) A carboxylic acid reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate to give brisk effervescence of carbon dioxide gas but an alcohol does not react with sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Question 30:
Name the functional group of organic compounds that can be hydrogenated. With the help of a suitable example, explain the process of hydrogenation, mentioning the conditions of the reaction and any one change in physical property with the formation of the product. Name any one natural source of organic compounds that are hydrogenated.
Solution :
Alkenes can be hydrogenated.
The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to obtain a saturated hydrocarbon is called hydrogenation.
Example: Ethene reacts with hydrogen in the presence of finely divided nickel as catalyst to form ethane.
Liquid vegetable oils are hydrogenated into vegetable ghee (solid fat).![]()
Question 31:
(a) Name the gas evolved when ethanol reacts with sodium.
(b) What type of compound is formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of cone. H2SO4 ?
(c) What will you observe when dilute ethanoic acid and dilute hydrochloric acid are put on universal indicator paper, one by one ? What does it show ?
Solution :
(a) Hydrogen gas is evolved when ethanol reacts with sodium.
(b) Esters are formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of conc. H2SO4.
(c) Dilute ethanoic acid turns universal indicator paper to orange, showing that its pH is about 4 which tell us that ethanoic acid is a weak acid. On the other hand, dilute hydrochloric acid turns universal indicator paper to red, showing that its pH is about 1. This shows us that hydrochloric acid is a strong acid.
Question 32:
(a) What type of compound is CH3COOH ?
(b) What substance should be oxidised to prepare CH3COOH ?
(c) What is the physical state of CH3COOH ?
(d) State one advantage of soaps over detergents.
Solution :
(a) CH3COOH is a c arboxylic acid.
(b) Ethanol, CH3CH2OH should be oxidised to prepare CH3COOH.
(c) Liquid state
(d) Soaps are biodegradable whereas detergents are non-biodegradable.
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:264
Question 33:
(a) What happens when ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid in the presence of a little of concentrated sulphuric acid ? Write equation of the reaction involved.
(b) What happens when ethanol is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 170°C ? Write the equation of the reaction which takes place.
Solution :
Question 34:
(a) What happens when ethanol is oxidised with alkaline potassium permanganate (or acidified potassium dichromate) ? Write the equation of the reaction involved.
(b) Choose those compounds from the following which can turn blue litmus solution red :
HCHO, CH3COOH, CH3OH, C2H5OH, HCOOH, CH3CHO Give reasons for your choice.
Solution :
(a) When ethanol is oxidised with alkaline potassium permanganate (or acidified potassium dichromate), it gets oxidised to form ethanoic acid.
(b) CH3COOH and HCOOH can turn blue litmus solution red. These are organic acids.
Question 35:
(a) Explain the process of preparation of soap in laboratory.
(b) Why is common salt (sodium chloride) added during the preparation of soap ?
(c) Why is soap not suitable for washing clothes when the water is hard ?
Solution :
(a) Soap can be prepared in the laboratory as follows:
1. Take about 20 ml of castor oil (cottonseed oil, linseed oil or soya bean oil) in a beaker.
2. Add 30 ml of 20% sodium hydroxide solution to it.
3. Heat the mixture with constant stirring till a paste of soap is formed.
4. Then add 5 to 10 grams of common salt (sodium chloride).
5. Stir the mixture well and allow it to cool. On cooling the solution, solid soap separates out.
6. When the soap sets, it can be cut into pieces called ‘soap bars’.
(b) Common salt is added to the mixture to make the soap come out of solution. Though most of the soap separates out on its own but some of it remains in solution. Common salt is added to precipitate out all the soap from the aqueous solution.
(c) When soap is used for washing clothes with hard water, a large amount of soap in water is reacting with the calcium and magnesium ions of hard water to form an insoluble precipitate called scum, before it can be used for the real purpose of washing.
Question 36:
(a) What happens when methane (natural gas) burns in air ? Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
What happens when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate ? Write chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil.
Solution :
Question 37:
(a) Describe, giving equation, a chemical reaction which is characteristic of saturated hydrocarbons (or alkanes).
What is an oxidising agent ? Name two oxidising agents which can oxidise ethanol to ethanoic acid.
Describe one reaction of a carboxylic acid.
Solution :
Question 38:
(a) Write names and formulae of hydrocarbons containing a single and a double bond (one example for each). Give one characteristic chemical property of each.
(b) What is a detergent ? Name one detergent.
(c) Why have detergents replaced soap as a washing agent ?
Solution :
(a) (i) Single bond: Methane, CH4. They are quite unreactive hence they undergo substitution reaction with chlorine in presence of sunlight.
(ii) Double bond: Ethene, CH2=CH2. They undergo addition reaction in the presence of a catalyst like nickel or palladium.
(b) A detergent is the sodium salt of long chain benzene sulphonic acid which has cleansing properties in water. Ex: Sodium n-dodecyl benzene sulphonate.
(c) Detergents are better cleansing agents than soaps because they do not form insoluble calcium and magnesium salts with hard water, and hence can be used for washing even with hard water.
Question 39:
(a) How does ethanoic acid react with sodium hydrogencarbonate ? Give equation of the reaction which takes place.
(b) Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications ?
Which of the two is better for washing clothes when the water is hard : soap or detergent ? Give reason for your answer.
Solution :
Question 40:
(a) What is meant by a substitution reaction ? Give an example (with equation) of the substitution reaction of, an alkane.
(b) How is soap made ? Write a word equation involved in soap making.
Solution :
Question 41:
(a) How is ethanoic acid obtained from ethanol ? Write down the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
(b) How would you distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid by chemical test ?
(c) Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Solution :
Question 42:
(a) What happens when methane reacts with chlorine ? Give equation of the reaction which takes place.
(b) What is hydrogenation ? What is its industrial application ?
(c) Give any two differences between soaps and detergents.
Solution :
Question 43:
(a) What happens when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide ? Write equation of the reaction involved.
(b) What happens when vegetable oils are hydrogenated ? Name the catalyst used.
(c) What is the advantage of detergents over soaps for washing clothes ? Also state one disadvantage.
Solution :
Question 44:
(a) An organic compound X of molecular formula C2H4O2 gives brisk effervescence with sodium hydrogencarbonate. Give the name and formula of X.
(b) A mixture of ethyne (acetylene) and oxygen is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used ?
(c) Name a chemical reaction which is characteristic of unsaturated hydrocarbons (like alkenes and alkynes).
Solution :
(a) Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH gives brisk effervescence with sodium hydrogencarbonate.
(b) A mixture of ethyne and air is not used for welding because burning of ethyne in air produces a sooty flame (due to incomplete combustion) which is not hot enough to melt metals for welding.
(c) Addition reactions are a characteristic of unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Question 45:
(a) What is meant by an addition reaction ? Give an example (with equation) of an addition reaction of an alkene.
(b) What is added to groundnut oil when it is to be converted to vanaspati ghee ?
(c) Which of the two is better for our health : butter or vegetable oil ? Why ?
Solution :
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:265
Question 46:
(a) When ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate, then a salt X is formed and a gas Y is evolved.
Name the salt X and gas Y. Describe an activity with the help of a labelled diagram of the apparatus used to prove that the evolved gas is the one which you have named. Also write the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
(b) Give any two uses of ethanoic acid.
Solution :
(a)Salt X is sodium ethanoate, CH3COONa; Gas Y is carbon dioxide, CO2
Activity: Take a boiling tube and put about 0.5 g of sodium carbonate in it. Add 2 ml of dilute ethanoic acid to the boiling tube (through a thistle funnel). We will observe that brisk effervescence of carbon dioxide gas is produced. Let us pass this gas through lime water taken in a test tube. We will find that lime water turns milky. Only carbon dioxide gas can turn lime water milky. So, this experiment proves that when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate, then carbon dioxide gas is evolved.
(b)(i) Dilute ethanoic acid (in the form of vinegar) is used as a food preservative in the preparation of pickles and sauces.
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of acetone and esters used in perfumes.
(a) Activity:
(i) Take 1 ml of pure ethanol (absolute alcohol) in a test-tube and add 1 ml of glacial ethanoic acid to it. Then add 2 or 3 drops of concentrated sulphuric acid to the mixture.
(ii) Warm the test-tube containing above reaction mixture in hot water bath (a beaker containing hot water) for about 5 minutes.
(iii) Pour the contents of the test-tube in about 50 ml of water taken in another beaker and smell it.
(iv) A sweet smell is obtained indicating the formation of an ester.
Reaction:
(c) Uses of esters:
(i) Esters are used in making artificial flavours and essences. These are used in cold drinks, ice-creams, sweets and perfumes.
(ii) Esters are used as solvents for oils, fats, gums, resins, cellulose, paints, varnishes, etc.
Question 48:
(a) Name the reaction which is usually used in the conversion of vegetable oils to fats. Explain the reaction
involved in detail. Write a chemical equation to illustrate your answer.
(b) What is saponification ? Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved in this process. Name all the substances which take part in this process and also those which are formed.
(c) Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water ? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents like ethanol also ?
Solution :
Question 49:
(a) What is a soap ? Name one soap.
(b) Describe the structure of a soap molecule with the help of a diagram.
(c) Explain the cleansing action of soap. Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
Solution :
(a) A soap is the sodium salt (or potassium salt) of a long chain carboxylic acid (fatty acid) which has cleansing properties in water.
Example: Sodium stearate, C17H35COO–Na+
(b) A soap molecule has two parts: the long chain organic part and the ionic part containing the -COO–Na+ group. It has to be remembered that this is not an ion, the atoms are all covalently bonded, the electrical charges show how the charges get polarized in the group. A soap molecule has a tadpole like structure shown below:
(c) Cleaning action of soap has been explained with the help of the image below:
Soaps are molecules in which the two ends have differing properties, one is hydrophilic, that is it dissolves in water, while the other end is hydrophobic, that is it dissolves in hydrocarbons. When soap is at the surface of water, the hydrophobic ‘tail’ of soap will not be soluble in water and the soap will align along the surface of water with the ionic end in water and the hydrocarbon ‘tail’ protruding out of water.
Inside water, these molecules have a unique orientation that keeps the hydrocarbon portion inside the water. This is achieved by forming clusters of molecules in which the hydrophobic tails are in the interior of the cluster and the ionic ends are on the surface of the cluster. This formation is called a micelle. When a dirty cloth is put in water containing dissolved soap, then soap in the form of a micelle is able to clean. The hydrocarbon ends of the soap attach to the oily dirt particles and entrap them at the centre of the micelle. the ionic ends in the micelles remain attached to water. When the dirty cloth is agitated in soap solution, the oily dirt particles entrapped by soap micelles get dispersed in water and the cloth gets cleaned.
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:266
Question 66:
A neutral organic compound X of molecular formula C2H6O on oxidation with acidified potassium dichromate gives an acidic compound Y. Compound X reacts with Y on warming in the presence of cone. H2S04 to give a sweet smelling substance Z. What are X, Y and Z ?
Solution :
X is ethanol
Y is ethanoic acid
Z is ethyl ethanoate
Ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid to form ethyl ethanoate ester.
Question 67:
Consider the following organic compounds :
HCHO, C2H5OH, C2H6, CH3COOH, C2H5C1
Choose two compounds which can react in the presence of cone. H2S04 to form an ester. Give the name and formula of the ester formed.
Solution :
C2H5OH and CH3COOH react in the presence of conc. H2SO4 to form an ester. Ethyl ethanoate, CH3COOC2H5 is formed in the reaction.
Question 68:
A neutral organic compound is warmed with some ethanoic acid and a little of cone. H2S04. Vapours having sweet smell (fruity smell) are evolved. What type of functional group is present in this organic compound ? The structural formula of an ester is :
Solution :
Alcohol group, -OH. Acids react with alcohols to form sweet smelling esters.
Question 69:
The structural formula of an ester is :
Write the formula of the acid and the alcohol from which it is formed.
Solution :
Question 70:
Consider the following organic compounds :
CH3OH, C2H5OH, CH3COCH3, CH3COOH, C2H5COOH, C4H9COOC2H5, CH4, C2H6, CH3CHO, HCHO Out of these compounds :
(a) Which compound is most likely to be sweet-smelling ?
(b) Which compound on treatment with cone. H2S04 at 170°C forms an alkene ?
(c) Which compound on repeated chlorination forms chloroform ?
(d) Which compound is added to alcohol to denature it ?
(e) Which compound is a constituent of vinegar ?
(f) Which compound is used to sterilise wounds and syringes ?
Solution :
(a) C4H9COOC2H5; Ester
(b) C2H5OH; Alcohol forms ethene, C2H4
(c) CH4; Methane
(d) CH3OH; Methanol
(e) CH3COOH; Acetic acid
(f) C2H5OH; Ethanol
Question 71:
An organic acid X is a liquid, Which often freezes during winter time in cold countries, having the molecular formula C2H402. On warming it with methanol in the presence of a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid, a compound Y with a sweet smell is formed.
(a) Identify X and Y. Also write their formulae showing the functional group present in them.
(b) Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Solution :
Question 72:
An organic compound A having the molecular formula C3H8O is a liquid at room temperature. The organic liquid A reacts with sodium metal to evolve a gas which burns causing a little explosion. When the organic liquid A is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 170°C, it forms a compound B which decolourises bromine water. The compound B adds on one molecule of hydrogen in the presence of Ni as catalyst to form compound C which gives substitution reactions with chlorine.
(a) What is compound A ?
(b) What is compound B ?
(c) What type of reaction occurs when A is converted into B ?
(d) What is compound C ?
(e) What type of reaction takes place when B is converted into C ?
Solution :
(a) A is propanol, CH3-CH2-CH2OH
(b) B is propene, CH3CH=CH2
(c) Dehydration reaction
(d) C is propane, CH3CH2-CH3
(e) Addition reaction
Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Page No:267
Question 73:
An organic compound A (molecular formula C2H402) reacts with Na metal to form a compound B and evolves a gas which burns with a pop sound. Compound A on treatment with an alcohol C in the presence of a little of concentrated sulphuric acid forms a sweet-smelling compound D (molecular formula C3H602). Compound D on treatment with NaOH solution gives back B and C. Identify A, B, C and D.
Solution :
A is ethanoic acid, CH3COOH
B is sodium ethanoate, CH3COONa
C is methanol, CH3OH
D is methyl ethanoate, CH3COOCH3
Question 74:
Which of the following hydrocarbons can decolourise bromine water and which cannot ? Why ?
C6H12, C6H14, C6H10
Solution :
C6H12 and C6H10 c an decolourise bromine water since these are unsaturated hydrocabons.
C6H14 cannot decolourise bromine water since it is a saturated hydrocarbon.
Question 75:
A four carbon atoms containing neutral organic compound X reacts with sodium metal to evolve a gas which burns with a ‘pop’ sound. Another four carbon atoms containing carbon compound reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate to evolve a gas which turns lime water milky. When compounds X and Y are heated together in the presence of a little of concentrated sulphuric acid, then a new compound Z is formed.
(a) What is compound X ? Also write its formula.
(b) What is compound Y ? Also write its formula,.
(c) What is compound Z ? Also write its formula.
(d) What type of smell is given by compound Z ?
(e) What is the general name of compounds like Z ?
(f) What is the general name of the reaction which takes place between X and Y to form Z ?
Solution :
(a) X is butanol, C4H9OH
(b) Y is butanoic acid, C3H7COOH
(c) Z is butyl butanoate, C3H7COOC4H9
(d) Sweet smell is given by the compound Z.
(e) Esters
(f) Esterification reaction.
